A Complete Guide to Incoterms 2023: Everything You Need to Know
When it comes to international trade, one of the biggest challenges is navigating the complexities of shipping, customs clearance, and risk management. To help streamline these processes, Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are used globally to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. This guide will explain the importance of Incoterms, how they affect shipping costs, and what to consider when choosing the right one for your trade contracts.
1. What Are Incoterms in 2023?
Incoterms are a set of globally recognized rules established by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) to standardize international trade practices. They clarify the distribution of responsibilities and risk transfer between buyers and sellers. The most recent version, Incoterms 2020, defines key elements such as freight shipping, customs clearance, and insurance obligations.
Incoterms are updated every ten years to reflect evolving trade practices, with the latest edition—Incoterms 2020—being the current standard.
2. Why Are Incoterms So Important in International Trade?
International trade involves various complexities, including shipping logistics, taxes, customs duties, and insurance. Without clear guidelines, misunderstandings and disputes can arise. Incoterms help to resolve these issues by clearly defining the responsibilities of both the buyer and seller, ensuring that each party knows who is accountable for what.
Today, Incoterms are recognized by customs authorities and banks worldwide and are included in sales contracts and letters of credit, streamlining the trade process and minimizing risks for all involved.
3. How Do Incoterms Affect Shipping Costs?
Shipping costs can include basic transportation, insurance fees, and customs duties, but they may also involve additional charges like port handling and storage fees. The Incoterm used in a contract dictates who bears the responsibility for these costs.
For example:
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) places the burden of customs clearance and fees on the seller.
- EXW (Ex Works) shifts the responsibility to the buyer for customs clearance and payment.
Understanding which party is responsible for specific charges will help you avoid unexpected costs.
4. Which Incoterm Should You Use?
Choosing the right Incoterm depends on several factors:
- Budget: Do you have the resources to handle shipping and customs processes, or would you prefer the seller to take care of it?
- Cargo Type: Some goods may require special shipping arrangements.
- Experience: Are you familiar with international logistics and customs regulations?
For minimal responsibility, DDP is ideal, as the seller handles most of the process. If you have more control over shipping or want to manage it yourself, EXW might be a better fit.
5. What Do Incoterms Cover?
Incoterms address several aspects of international shipping:
- Delivery of Goods: Specifies where and when the seller must deliver the goods.
- Carriage of Goods: Defines who is responsible for transportation.
- Risk of Loss or Damage: Specifies when the risk shifts from seller to buyer.
- Insurance: Clarifies whether the seller needs to provide insurance.
- Customs Clearance: Details who handles export and import customs duties.
- Payment Obligations: States which party is responsible for payment at each stage.
These terms ensure clarity and reduce the chance of disputes during the shipping process.
6. What Do Incoterms Not Cover?
Incoterms do not address:
- Ownership Transfer of goods
- Intellectual Property Rights (e.g., patents, trademarks)
- Product Quality or Specifications
- Payment Methods or Due Dates
- Liability for Non-performance or contract breaches
These aspects typically need to be addressed in separate contracts or legal documents.
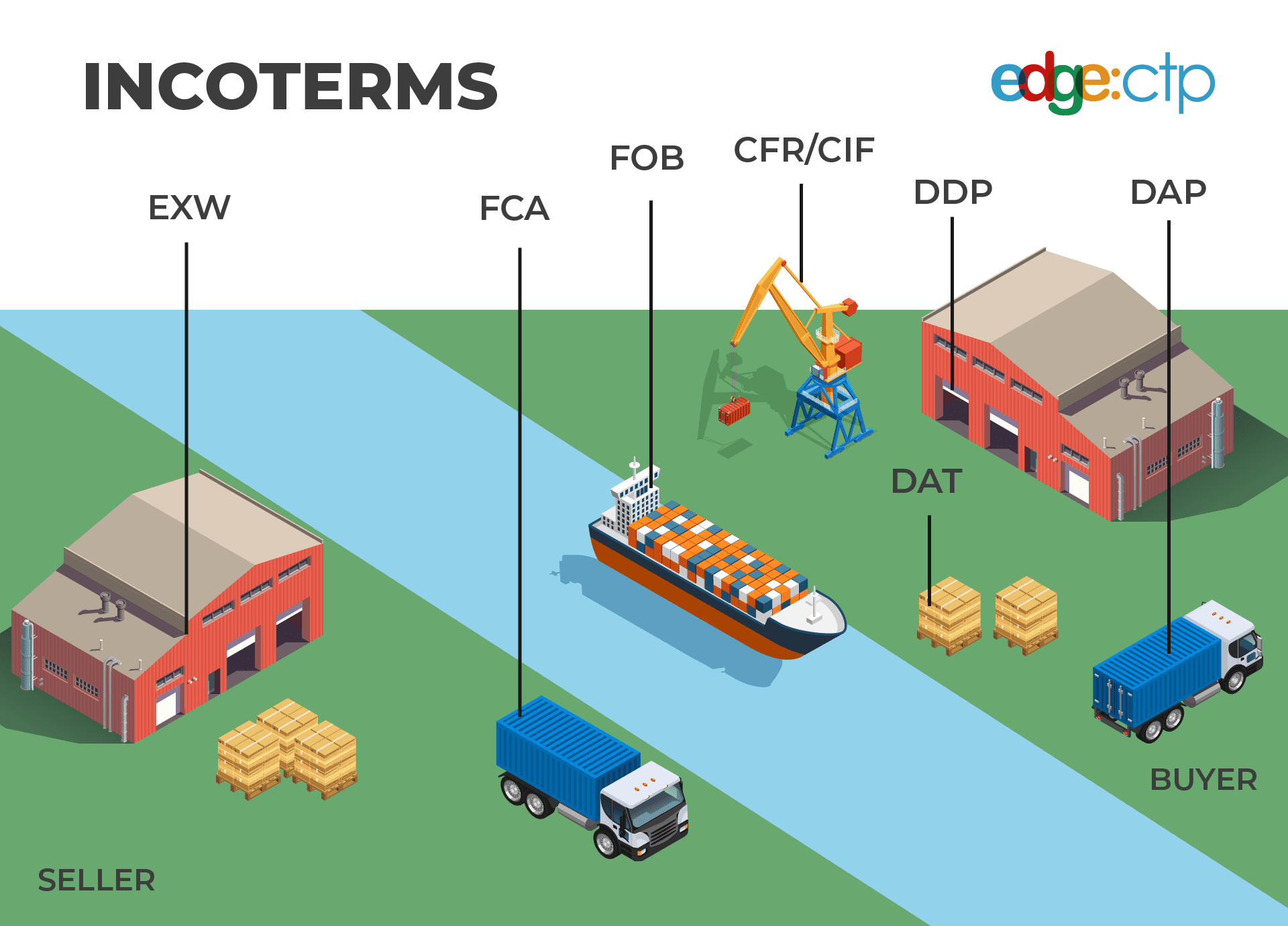
7. Incoterms 2023 Rules Explained in Detail
Here are some of the most commonly used Incoterms:
- EXW (Ex Works): The seller makes goods available at their premises; the buyer handles everything from there.
- FCA (Free Carrier): The seller delivers goods to a carrier nominated by the buyer.
- FOB (Free on Board): Seller delivers goods onboard the vessel; risk transfers to the buyer once goods are loaded.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight): Seller covers shipping and insurance costs to the destination port.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): The seller takes full responsibility for delivering the goods to the buyer's location, including all costs and duties.
Each term comes with different responsibilities and risks, so it's important to choose one that fits your needs.
8. How to Use Incoterms in Sales and Purchase Contracts
When drafting international sales contracts, it’s essential to specify which Incoterms version you are using (e.g., Incoterms 2020) and which terms apply. Different versions may have slightly different rules, so confirming the version helps avoid misunderstandings.
Most Incoterms are applicable to all modes of transport (e.g., road, rail, sea, air), but some terms, like FOB and CFR, are specific to sea freight.
9. Incoterms 2023 vs. Incoterms 2020
Although Incoterms 2020 is the most current version, some contracts may still reference Incoterms 2010. Ensure that the version is clearly stated in your contract to avoid confusion. The rules remain largely the same since the last update, but any discrepancies between versions should be resolved before finalizing a deal.
Conclusion
Incoterms provide a clear framework for international trade, ensuring that both buyers and sellers understand their responsibilities and risks. By choosing the right Incoterm for your contract, you can streamline the shipping process and avoid unexpected costs and complications. Be sure to stay updated on the latest rules and consult with trade professionals to ensure a smooth transaction.